Linear Congruent Generator
Overview
A Linear Congruent Generator, or LCG, is a
very common algorithm used to produce a sequence of
pseudorandom numbers.
An LCG is contained in many of the algorithms here,
including rline (rline), bigverb (bigverb),
sparse (sparse), and trand (trand).
The core API also has a global
RNG that is an LCG.
Wikipedia is a great resource on the subject: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_congruential_generator.
LCG parameters used in the sndkit LCGs come from this page.
Definition
A generalized LCG can be defined using the following expression:
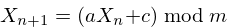
Where 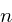 is the sample number,
is the sample number,
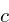 is the
is the increment,
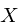 is the state,
is the state,
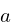 is the
is the multiplier, and
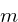 is the modulus.
is the modulus.
Typical Implementation in sndkit
Because sndkit favors self-contained algorithms, a similar LCG has been reimplemented many times. Fortunately, the algorithm itself is quite simple, and only requires a few lines of code with some magic numbers.
The typical implementation is a 32-bit LCG with a
multiplier a of 1103515245, increment c of
12345, and a modulus m of 2^31.
An LCG requires a 32-bit integer to store state. It can
also be helpful to have a constant of 2^31, which is
2147483648.
The C code can be reduced down to this expression;
unsigned long rng;
rng = seed;
rng = (1103515245 * rng + 12345) % 2147483648;Where seed is some initial seed, and rng is the state;